Powering the Future: How Field-Assisted Sintering is Revolutionizing Energy Applications
As industries seek more efficient, sustainable, and high-performance materials for energy applications, Field-Assisted Sintering (FAST) is emerging as a game-changing technology. Also known as Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), this advanced manufacturing process enables the rapid densification of materials using electrical current and pressure, creating superior components for energy storage, fuel cells, thermoelectric systems, and nuclear power applications.
From electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage to waste heat recovery and aerospace power systems, FAST is driving innovation in ways previously thought impossible.
What is Field-Assisted Sintering?
Unlike traditional sintering methods, which rely solely on heat, FAST accelerates the process by passing an electric current directly through the material. This method allows for:
- Lower sintering temperatures – preventing grain growth and preserving material properties.
- Faster processing times – sintering can be completed in minutes instead of hours.
- Denser, higher-purity materials – enhancing electrical, thermal, and mechanical performance.
These advantages make FAST particularly valuable in industries where high-performance materials are essential for energy generation, storage, and efficiency.
Energy Applications of FAST-Manufactured Materials
1. Battery Technology: More Power, Longer Life
The demand for high-performance lithium-ion and solid-state batteries is rising, especially in electric vehicles (EVs) and grid-scale energy storage. FAST is enabling the development of:
- Solid-state electrolytes – denser, more conductive ceramics for safer and more efficient batteries.
- Advanced anode and cathode materials – improving energy density and extending battery lifespan.
FAST-sintered materials are already making their way into next-generation EVs, smartphones, and renewable energy storage solutions.
2. Fuel Cells & Hydrogen Storage: Clean Energy Innovation
Hydrogen and fuel cell technologies are key players in the transition to clean energy, and FAST is helping these systems become more reliable and cost-effective.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) – used in clean power generation for homes, businesses, and industries, benefit from high-density ceramic electrolytes produced via FAST.
- Hydrogen Storage Systems – FAST enables the development of metal hydrides that store and release hydrogen more efficiently, improving fuel cell-powered vehicles and backup energy solutions.
3. Nuclear Energy: Safer and More Efficient Reactors
Nuclear power remains a leading source of low-carbon energy, and FAST is enhancing nuclear fuel and reactor materials in several ways:
- Advanced nuclear fuel pellets – FAST helps produce dense uranium, thorium, and accident-tolerant fuels for modern reactors.
- Radiation-resistant materials – critical for reactor components and long-term nuclear waste storage.
By improving the efficiency and safety of nuclear materials, FAST is supporting the next generation of clean, reliable nuclear power.
4. Thermoelectric Materials: Converting Waste Heat into Power
Thermoelectric generators (TEGs) convert heat into electricity, offering a powerful solution for waste heat recovery in industrial processes, automotive exhaust systems, and power plants.
FAST is enabling the production of high-performance thermoelectric materials such as:
- Bismuth telluride – used in cooling systems and wearable electronics.
- Silicon-germanium – found in aerospace and deep-space power applications.
- Skutterudites – enhancing efficiency in industrial heat recovery systems.
By capturing wasted heat and turning it into electricity, these materials play a key role in improving energy efficiency and sustainability.
5. Supercapacitors & Grid-Scale Energy Storage
FAST is also revolutionizing energy storage by producing high-performance electrode materials for supercapacitors and smart grids.
- Supercapacitors – FAST enhances nano-structured electrodes, enabling faster charge and discharge cycles for portable power solutions, industrial backup systems, and electric grid stabilization.
- Grid-scale energy storage – FAST-sintered materials support renewable energy integration, helping store excess solar and wind power for later use.
These advancements are paving the way for smarter, more resilient energy systems worldwide.
The Future of Energy with FAST Technology
The energy sector is undergoing a rapid transformation, and Field-Assisted Sintering is at the forefront of this revolution. By enabling the production of stronger, denser, and more efficient materials, FAST is driving innovations that impact:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) & Sustainable Transport
- Renewable Energy & Grid Storage
- Hydrogen Fuel & Clean Power Solutions
- Waste Heat Recovery & Industrial Efficiency
- Nuclear Power & Next-Gen Energy Systems
As more industries adopt FAST-based materials, the potential for cleaner, more efficient, and longer-lasting energy solutions will continue to grow. Companies like California Nanotechnologies are leading the charge, leveraging FAST technology to develop advanced materials that power the future.
Are you ready to explore how FAST-manufactured materials can enhance your energy applications? The future of energy starts now.
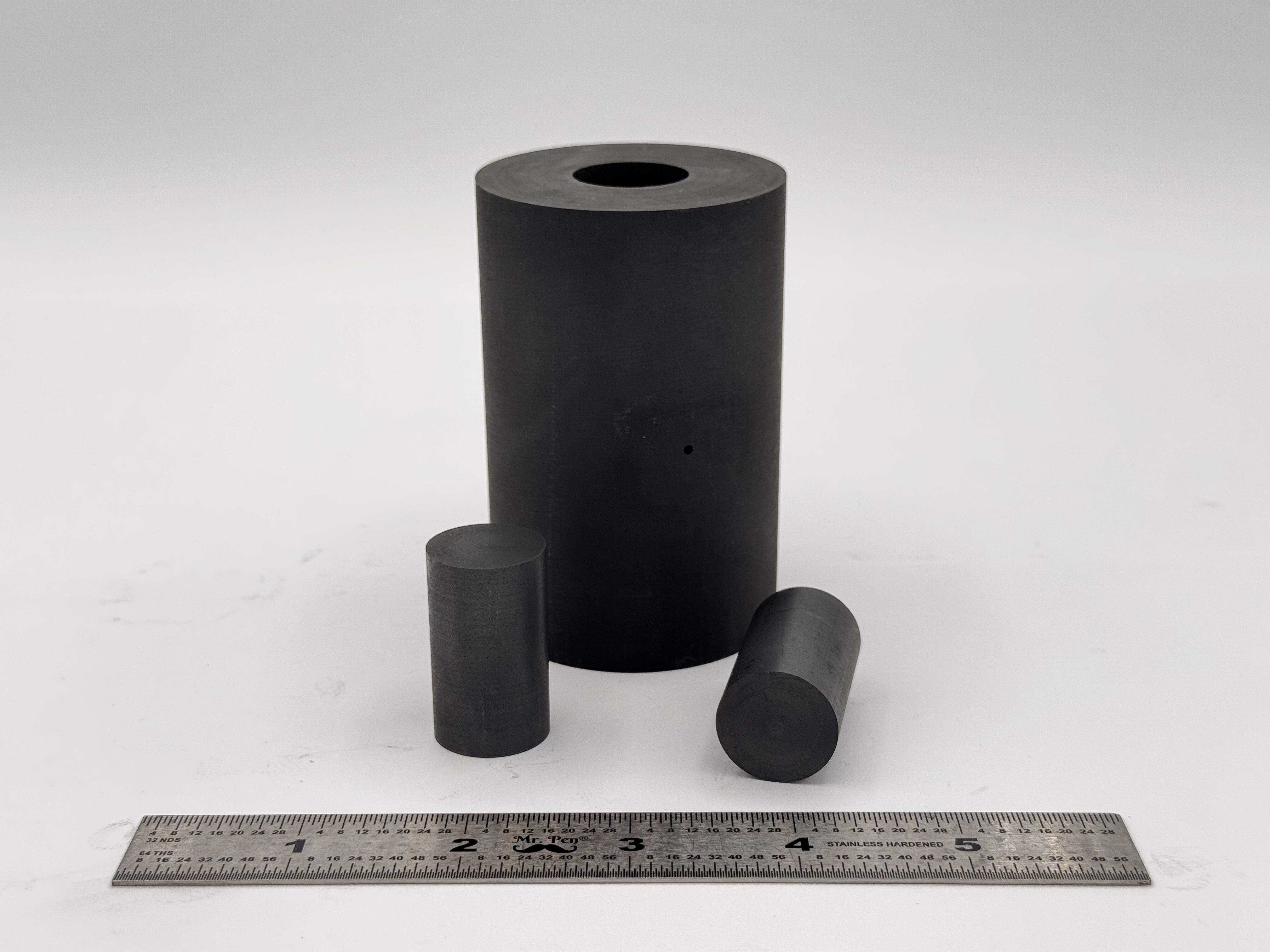 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling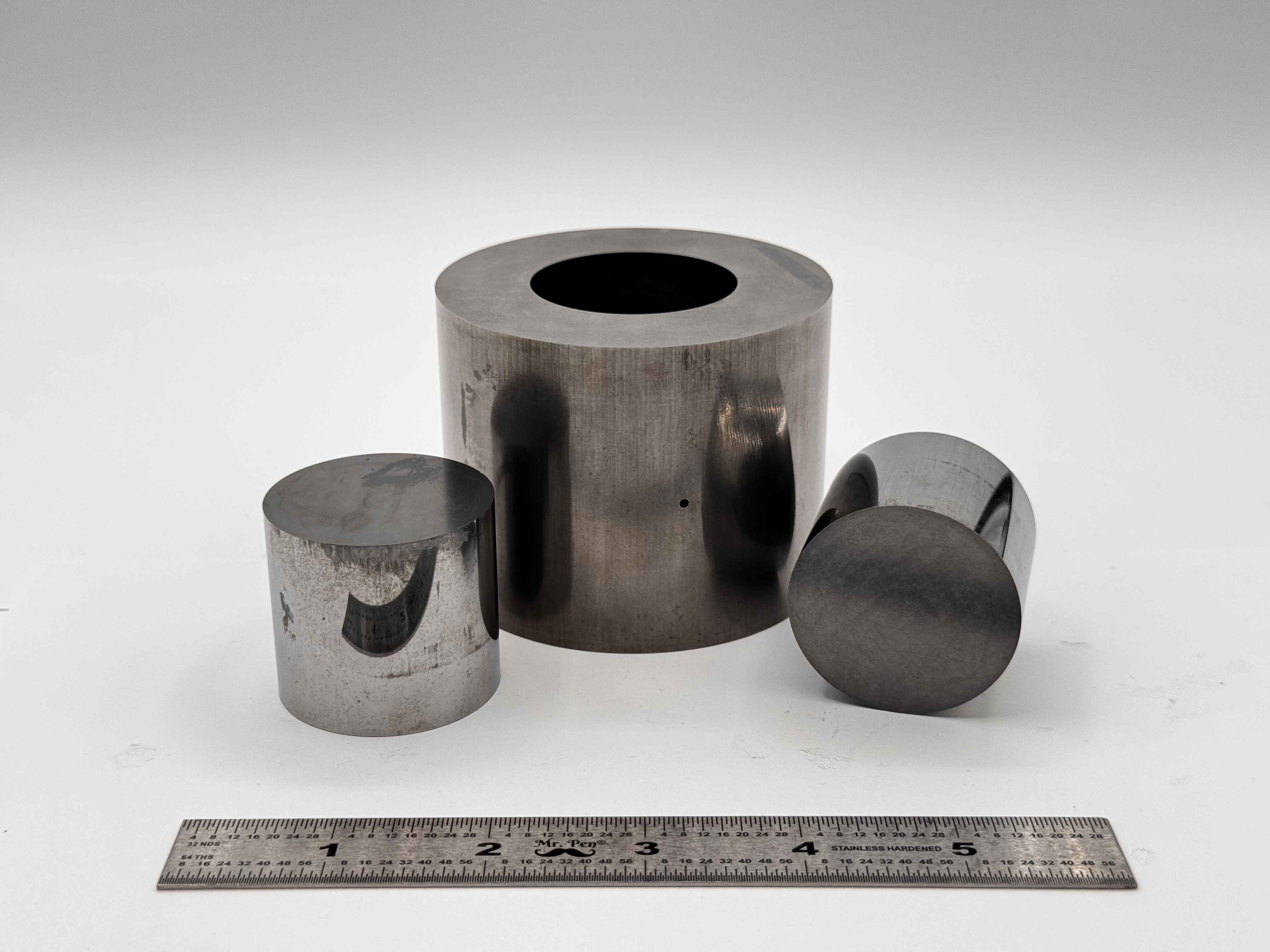 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software