Tungsten Carbide Dies: Unveiling Their Multifaceted Applications
Tungsten carbide dies, often hailed as one of the unsung heroes of manufacturing, play a crucial role in shaping, cutting, and forming a wide range of materials. These versatile tools are highly regarded for their durability and precision, making them indispensable in various industries.
What Is Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten carbide, also known as cemented carbide, is a composite material composed of tungsten (W) and carbon (C). It's known for its exceptional hardness, excellent wear resistance, and impressive strength. Tungsten carbide is synthesized by combining powdered tungsten and carbon in a sintering process, resulting in a material that is second only to diamonds in terms of hardness.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Dies
Wire Drawing
Wire drawing is one of the most common applications of tungsten carbide dies. In this process, a metal wire is pulled through a die to reduce its diameter while maintaining its length. Tungsten carbide dies are favored for this purpose due to their outstanding hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. This makes them ideal for shaping various types of wires, such as copper, steel, and aluminum, used in electrical cables, steel cords, and other products.
Tube Drawing
Similar to wire drawing, tube drawing involves reducing the diameter of tubes or pipes while preserving their length. Tungsten carbide dies are preferred for this task, as they can withstand the high pressures and temperatures associated with this process. This application is essential in industries like plumbing, automotive, and aerospace, where precision tubes are in high demand.
Cold Heading
Cold heading is a manufacturing process where metal blanks are formed into various shapes by applying high pressure. Tungsten carbide dies are vital in this process due to their ability to maintain their shape under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. The automotive and fastener industries heavily rely on cold heading to produce components like bolts, screws, and rivets.
Extrusion
Tungsten carbide dies find applications in extrusion processes where materials are forced through a die to create complex shapes or profiles. Industries such as construction, aerospace, and the manufacture of aluminum and plastic products utilize this process for creating structural components and intricate designs.
Powder Compaction
Powder metallurgy is an essential manufacturing technique for producing intricate metal parts and components. Tungsten carbide dies are used to compact metal powders into the desired shapes before sintering. This process is vital in the production of gears, bearings, and other high-precision mechanical components.
Coining and Stamping
Tungsten carbide dies are utilized in coining and stamping operations to create intricate patterns or engravings on metal surfaces. The minting of coins and the manufacturing of jewelry and decorative metal objects heavily rely on these dies for precision and durability.
Benefits of Tungsten Carbide Dies
- Exceptional Durability: Tungsten carbide dies are renowned for their long-lasting performance, reducing downtime and tool replacement costs.
- Precision: These dies enable the production of high-precision components, ensuring consistency and quality in manufacturing processes.
- Wear Resistance: Tungsten carbide's resistance to wear and abrasion means less frequent maintenance and longer tool life.
- Versatility: Tungsten carbide dies can be tailored to suit a wide range of materials, making them adaptable to various industries.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide dies have earned their place as indispensable tools in the world of manufacturing. Their applications span across numerous industries, from wire drawing to tube drawing, cold heading to powder compaction, and many more. With their exceptional durability, precision, and resistance to wear, tungsten carbide dies are essential for the production of high-quality components and products. As manufacturing continues to evolve, these versatile tools will remain at the forefront of the industry, enabling the creation of innovative and precise products across the globe.
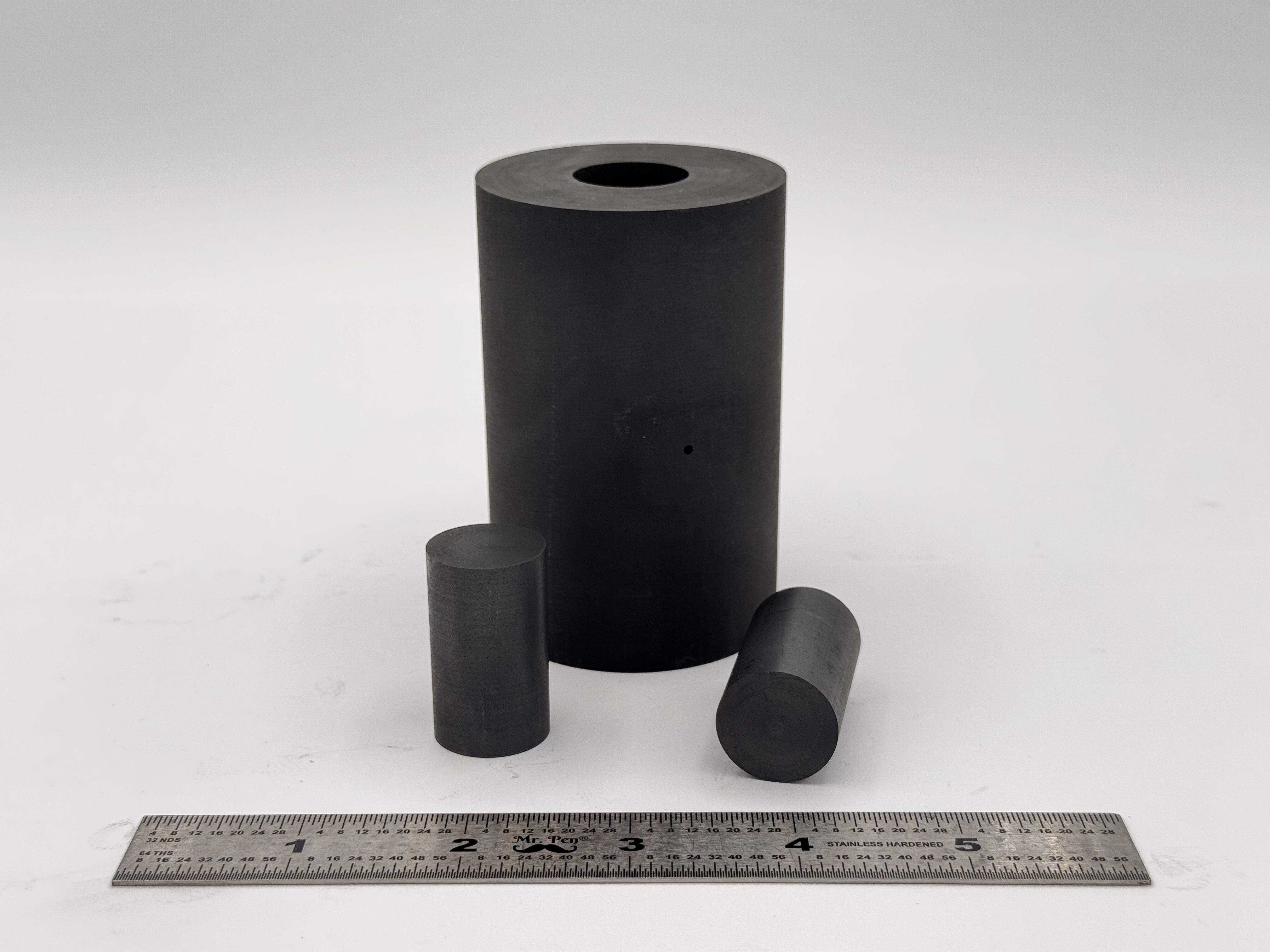 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling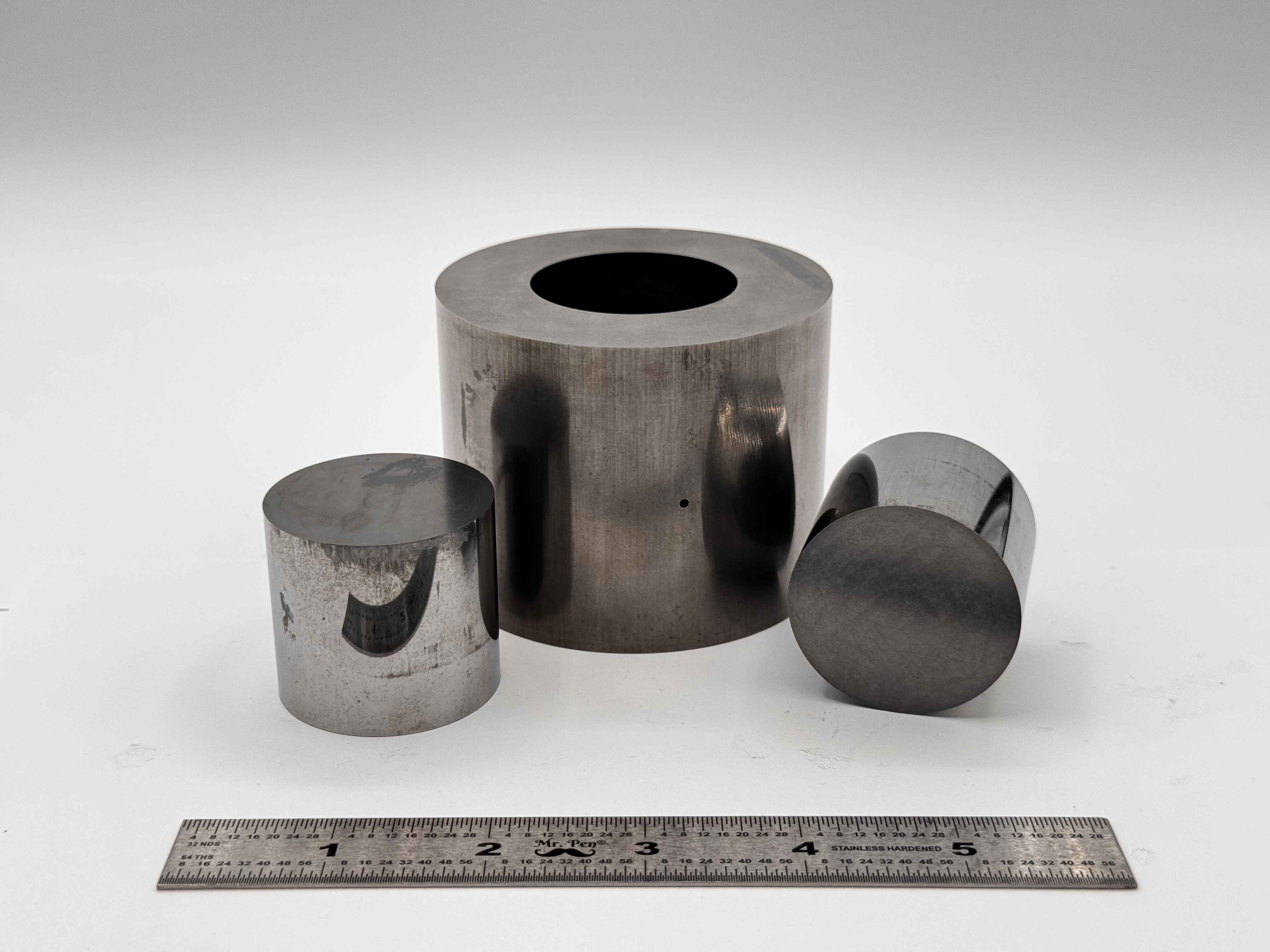 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software