Unleashing the Power of Spark Plasma Sintering: Transforming Industrial Manufacturing and Beyond
Introduction:
In the world of industrial manufacturing, technological advancements continue to reshape traditional processes, enabling the development of advanced materials with superior properties. One such groundbreaking innovation is the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system. This article aims to define and explore the applications of the Spark Plasma Sintering system in industrial manufacturing, while also delving into other industries that can benefit from this transformative technology.
Understanding Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) System:
The Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system is a revolutionary technology that facilitates the consolidation and densification of powders into solid materials through the application of pulsed electrical currents and pressure. Unlike traditional sintering methods, SPS operates at significantly lower temperatures and shorter processing times while offering enhanced material properties. This process involves the direct application of electrical current and pressure, promoting rapid diffusion and bonding of particles, resulting in materials with exceptional density, strength, and tailored microstructures.
Applications in Industrial Manufacturing:
The Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system has emerged as a game-changer in industrial manufacturing, offering numerous advantages and applications across a wide range of sectors. Here are some key industries that can leverage the benefits of SPS:
Aerospace and Defense:
The aerospace and defense industries require materials with superior mechanical properties, high temperature resistance, and excellent wear characteristics. SPS enables the fabrication of complex geometries and lightweight components, making it ideal for producing turbine blades, heat shields, and structural parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
Automotive and Transportation:
In the automotive sector, SPS has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing of automotive components. The technology enables the production of parts with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. Applications include engine components, brake pads, exhaust systems, and transmission components, leading to improved performance, durability, and fuel efficiency.
Electronics and Semiconductors:
With the constant demand for miniaturization and improved performance in electronic devices, SPS offers a promising solution. The system allows for the production of highly dense and fine-grained materials with excellent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and tailored dielectric properties. This makes it valuable for manufacturing electronic packaging, interconnects, sensors, and semiconductors.
Medical and Biotechnology:
The medical and biotechnology sectors benefit greatly from the capabilities of the SPS system. The technology enables the fabrication of biomedical implants, dental restorations, and drug delivery systems with tailored properties and controlled porosity. SPS-produced materials exhibit superior biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Energy and Renewable Technologies:
In the quest for cleaner and more efficient energy solutions, SPS plays a crucial role. The system facilitates the production of advanced materials for energy storage devices, fuel cells, solar cells, and thermoelectric generators. SPS-produced materials exhibit enhanced electrical and ionic conductivity, improved chemical stability, and optimized performance, thus advancing renewable energy technologies.
Conclusion:
The Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system has revolutionized industrial manufacturing by offering a highly efficient and versatile approach to fabricating advanced materials. From aerospace and automotive industries to electronics, medical, and renewable energy sectors, SPS finds diverse applications, enabling the development of materials with exceptional properties. As this technology continues to advance, its impact on various industries is set to reshape manufacturing and pave the way for a new era of innovation.
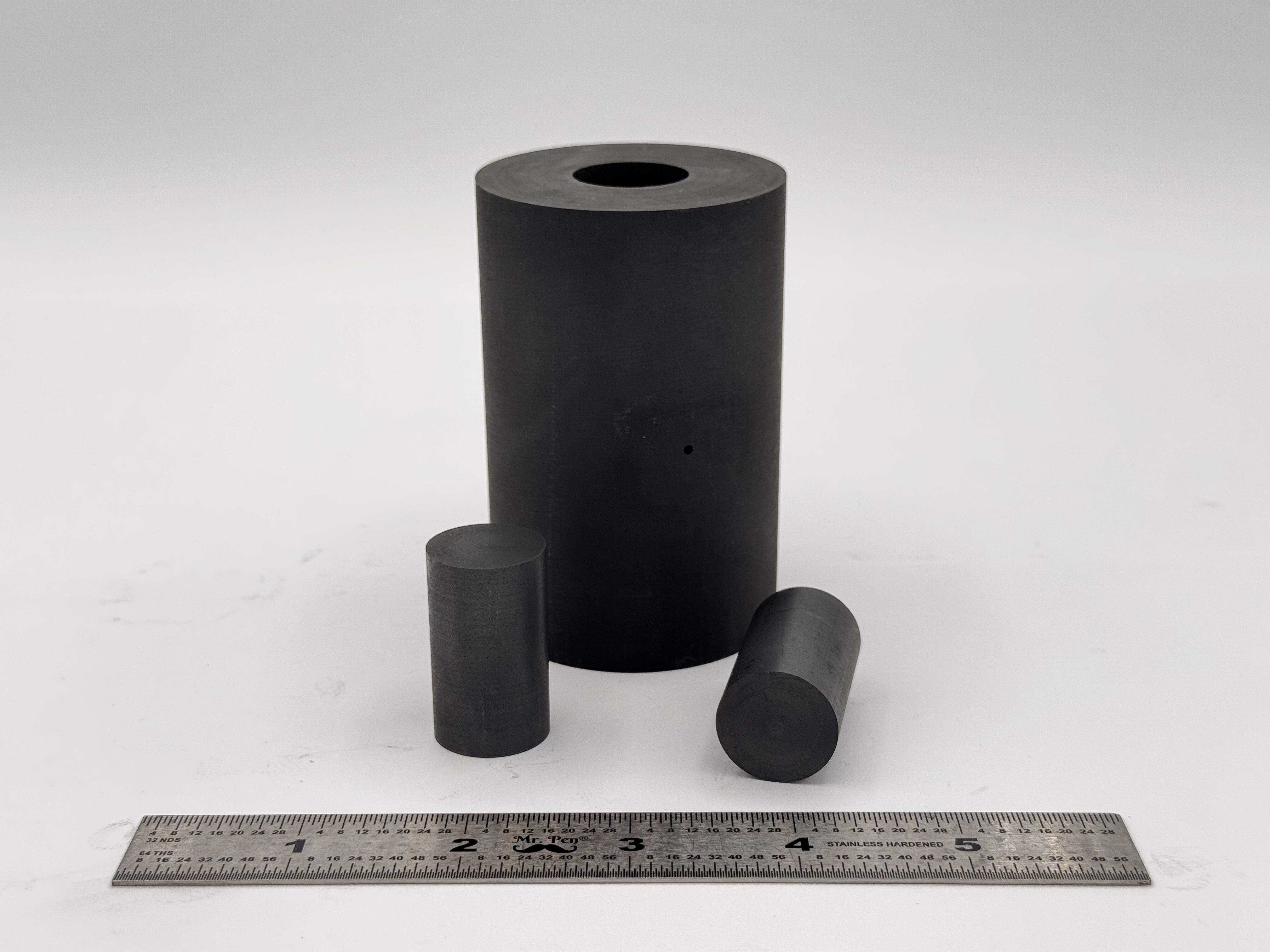 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling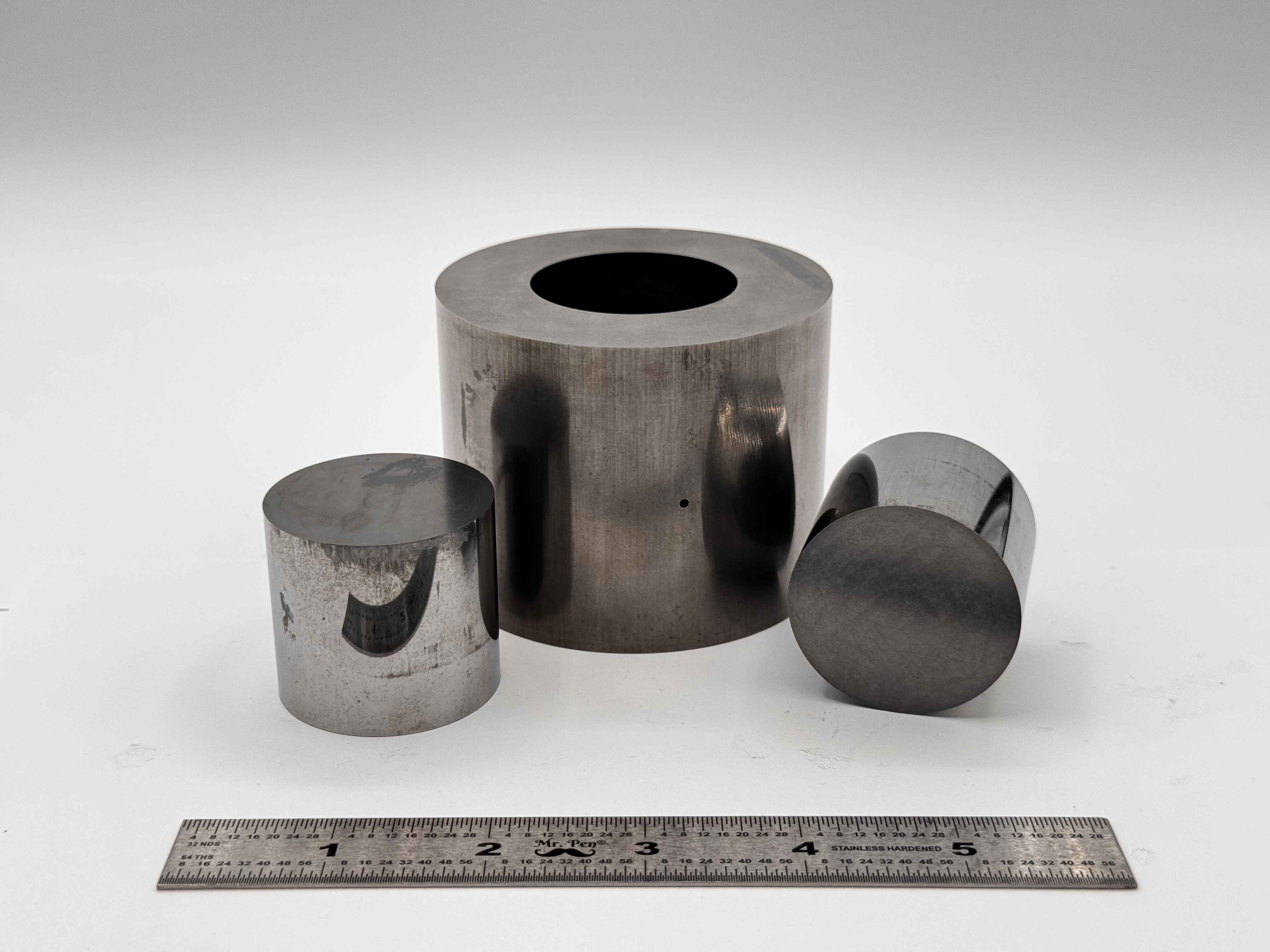 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems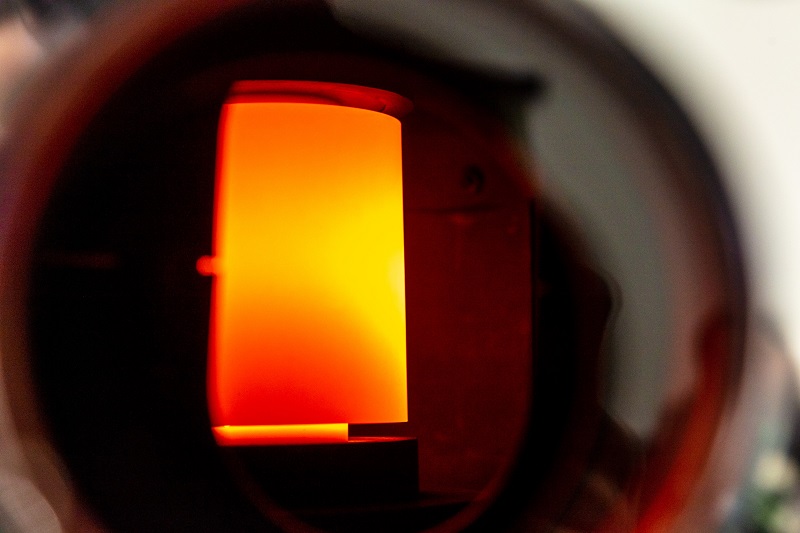 SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software