Cal Nano Services
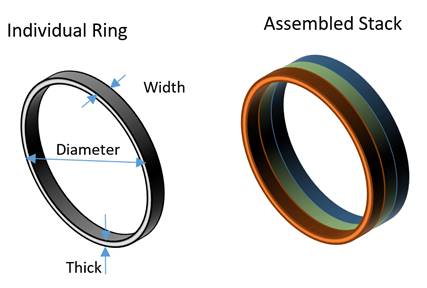
Diffusion Bonding
Diffusion bonding is a solid-state joining process used to bond similar or dissimilar materials by promoting atomic diffusion at the bonding interface. It involves applying heat and pressure to bring the surfaces of the materials in contact, enabling atoms to migrate and form metallurgical bonds. The success of diffusion bonding relies on the interdiffusion of atoms across the interface, which leads to the creation of strong bonds with high integrity. The process typically occurs at temperatures below the melting point of the materials involved, minimizing the risk of thermal distortion or damage.
During diffusion bonding, the applied pressure brings the material surfaces into intimate contact, ensuring atomic proximity and facilitating interatomic diffusion. As the temperature increases, atoms begin to migrate from one material to the other, driven by concentration gradients and the desire to achieve thermodynamic equilibrium. Diffusion occurs across the interface, enabling atoms to rearrange and bond with atoms of the other material. This diffusion-driven atomic rearrangement leads to the formation of strong, metallurgical bonds with high bond strength and excellent mechanical properties. Diffusion bonding finds applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where it is utilized to join materials with different compositions, reduce the need for additional fasteners, and achieve seamless integration of dissimilar materials.
Learn more about how Cal Nano uses Spark Plasma Sintering (linked to SPS page) and Field Assited Sintering Tequniques to solve diffusion bonding challenges.
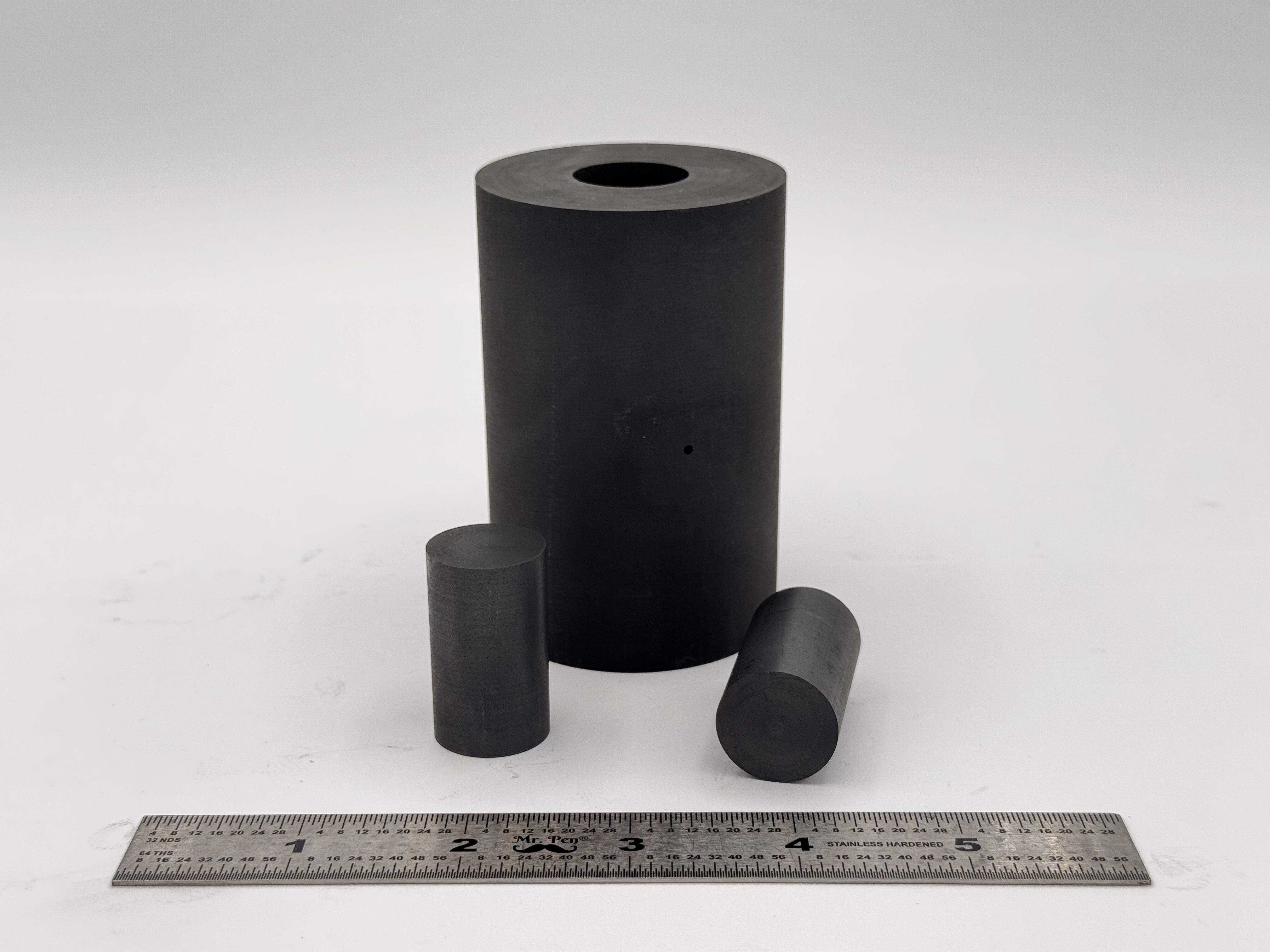 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling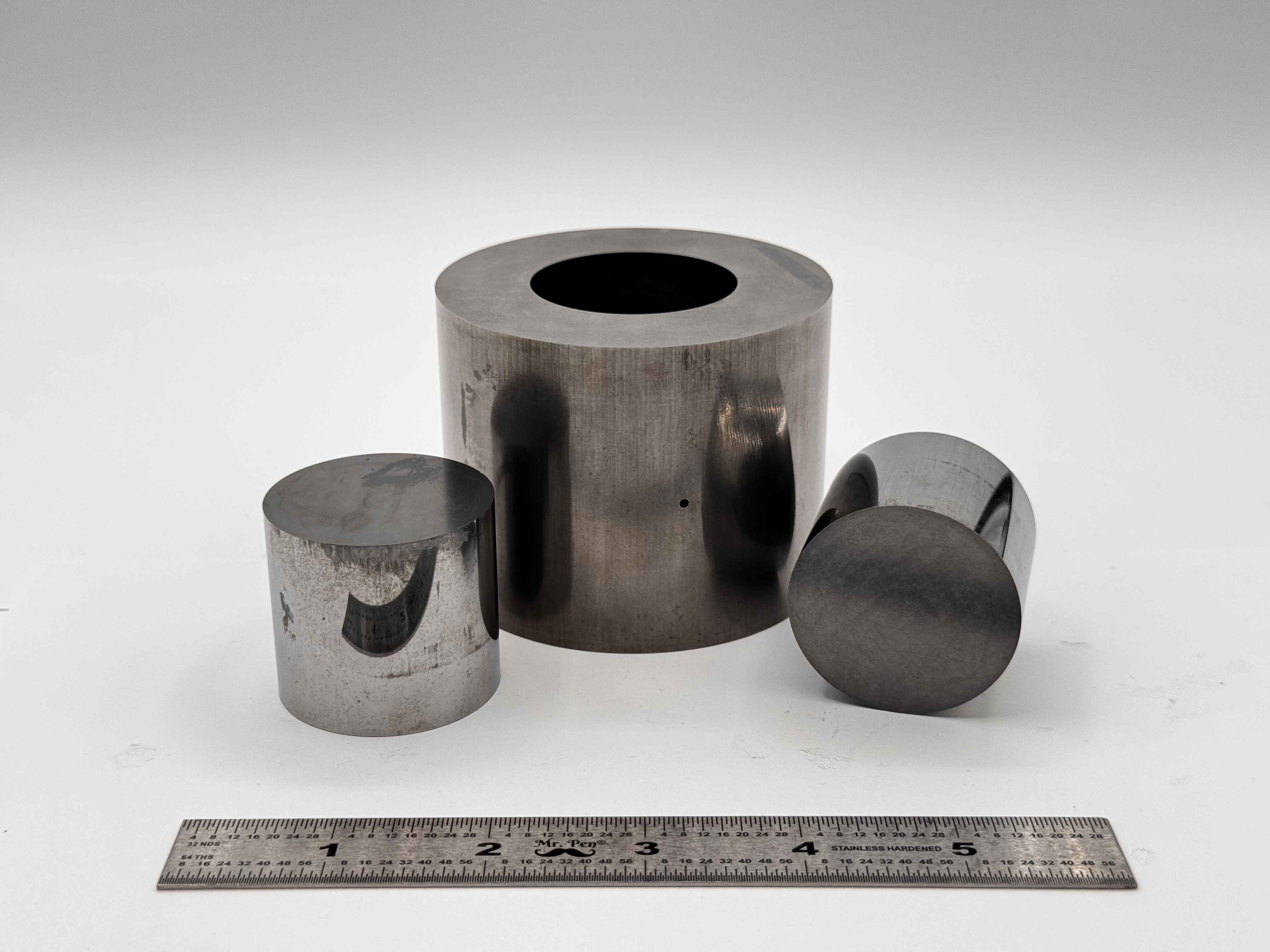 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software