Hot Pressing
Hot pressing is a specialized manufacturing process used to shape and consolidate materials by applying both heat and pressure simultaneously. It is commonly employed in the production of various ceramic, metal, and composite products. The process involves placing the raw material, typically in powder or preform form, into a die or mold and subjecting it to elevated temperatures and pressures. The combination of heat and pressure enables the material to undergo plastic deformation, resulting in enhanced densification and improved mechanical properties of the final product.
During hot pressing, the application of heat serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it facilitates the diffusion of atoms or molecules within the material, promoting atomic rearrangement and enabling the particles to bond more effectively. Additionally, elevated temperatures aid in reducing the viscosity of the material, making it more flowable and allowing for better filling of the mold cavities. Concurrently, pressure is applied to ensure intimate contact between the particles, promoting particle rearrangement and consolidation. This pressure-induced deformation leads to the elimination of voids and porosity, resulting in a more compact and structurally sound product. Overall, hot pressing offers a viable means to fabricate high-density, well-formed components with improved mechanical and physical properties, making it a valuable technique in various industrial applications.
At Cal Nano Hot Pressing is taken to the next level. Advancements compared to traditional Hot Pressing employed at Cal Nano include the application heating current directly to the containment tooling, mold, or even powder itself. These fundamental improvements make possible faster ramp rates, reduced hold times, better interparticle bonding, reduced production cycle times.
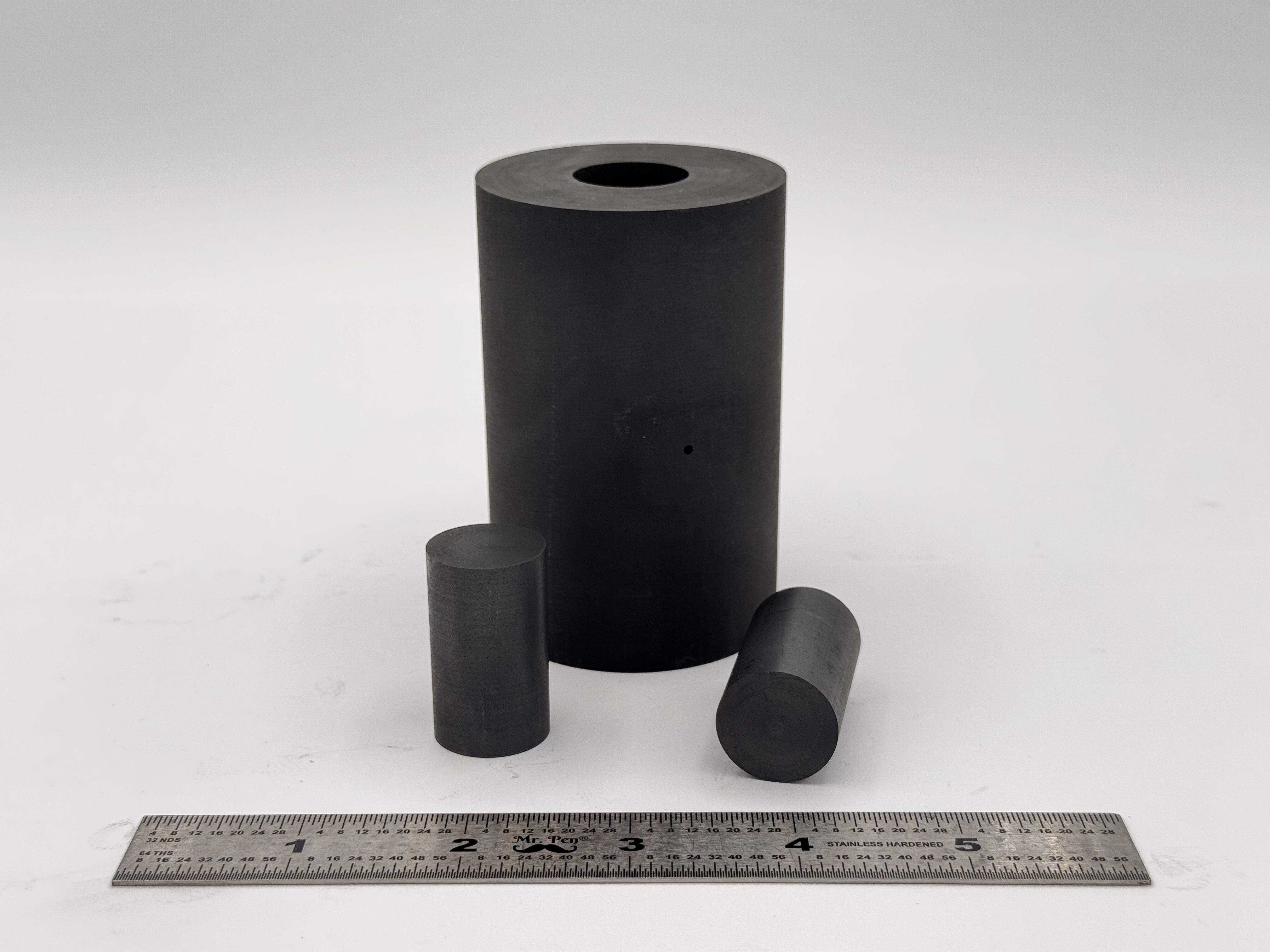 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling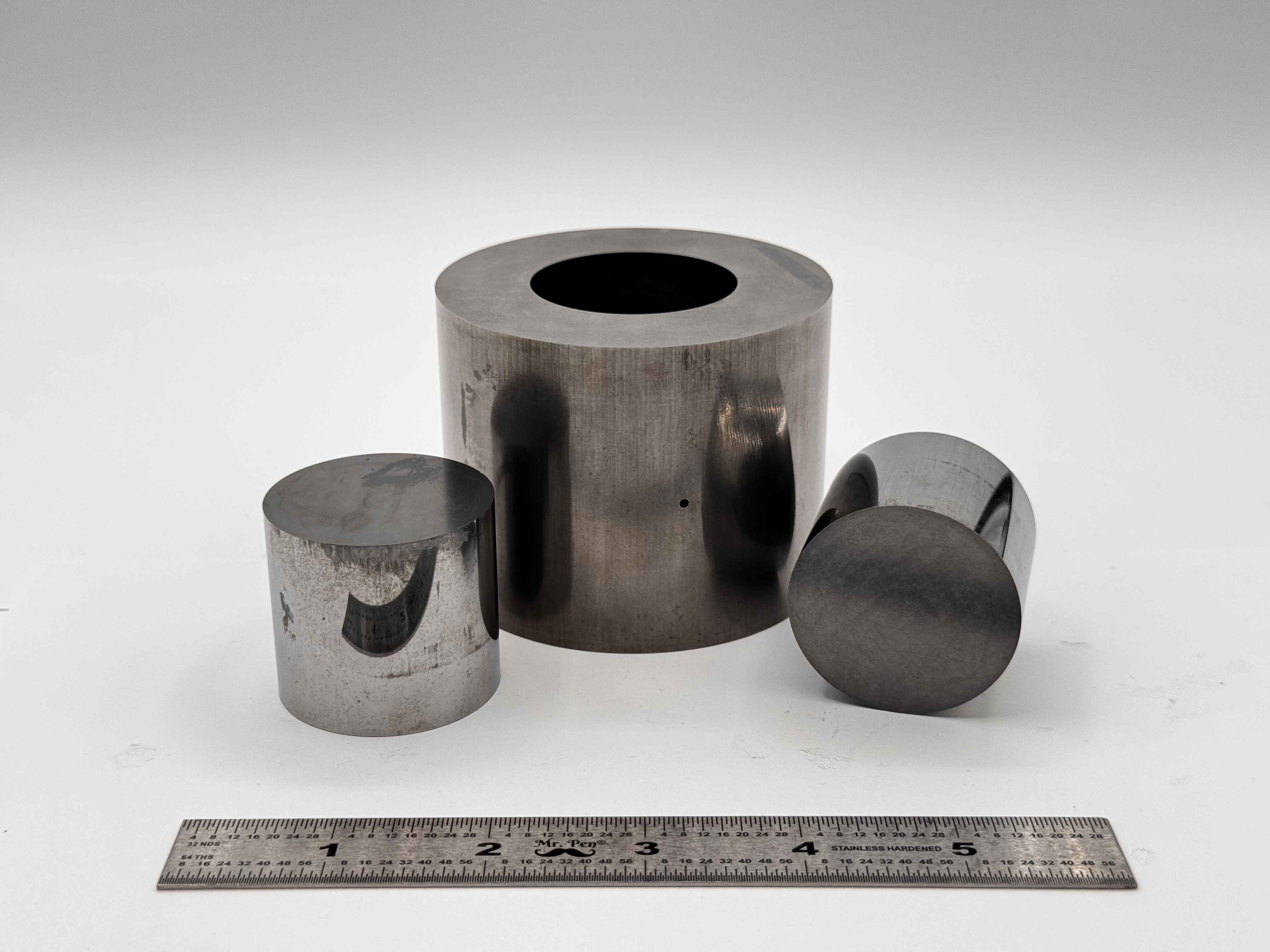 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems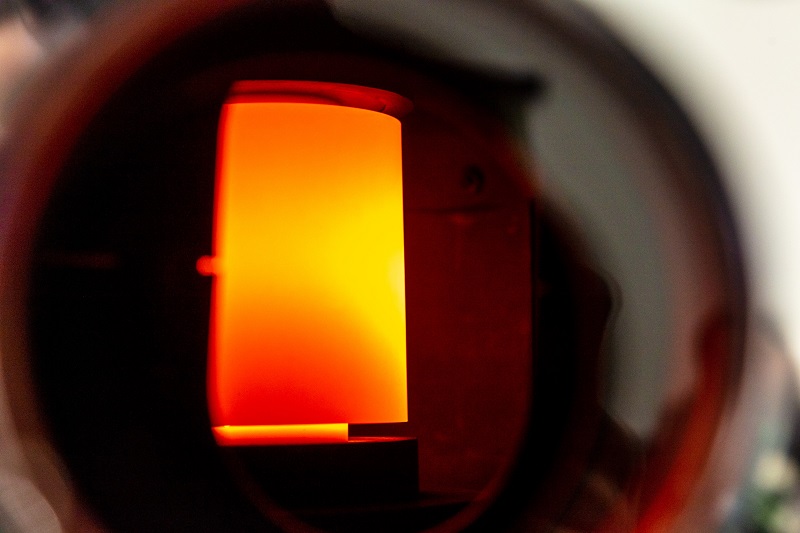 SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software